
the hierarchical catalogue of orthologs
Enabling
- Transfer of functional knowledge, e.g. from models to human.
- Learn biology from nature’s experimentation mutating genes.
Scope
- The broadest coverage of Eukaryotes / Prokaryotes / Viruses.
- Computed evolutionary traits and collated functional annotations.
Features
- Comparative charts,
- mapping of user data,
- interactive Web GUI,
- REST API, and SPARQL RDF.
TIP
To guess gene functions "by tradition" we recover gene families by their ancestry, and collate known biological roles of the family members.
TIP
The more closely related the species, the more finely-resolved the gene orthologies.
WARNING
We refer as orthologs to all descendants of a particular single gene of the last common ancestor, thus our operational definition refers to a specific phylogeny radiation for a set of species, termed the level-of-orthology.
# OrthoDB graphical abstract
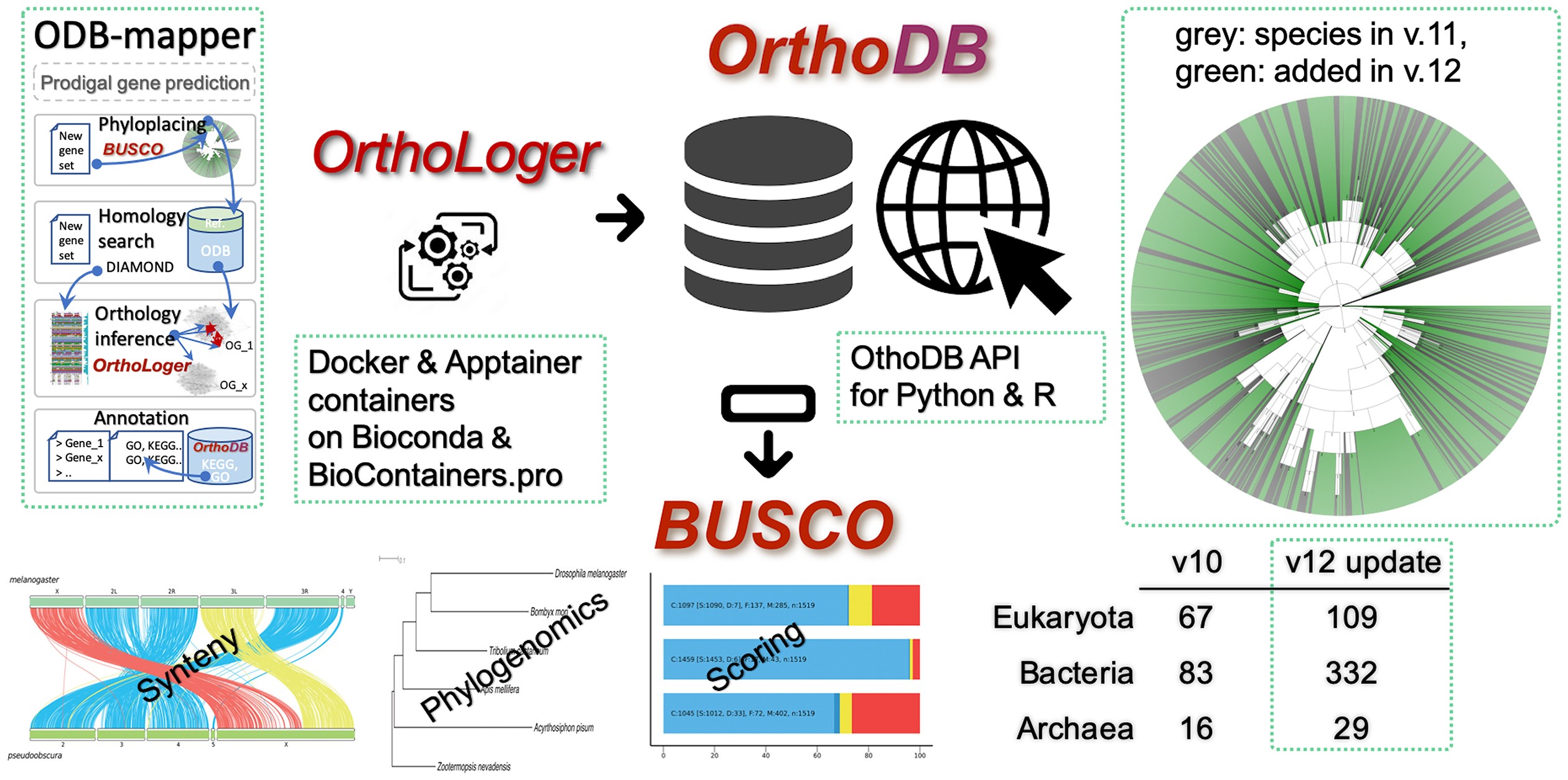
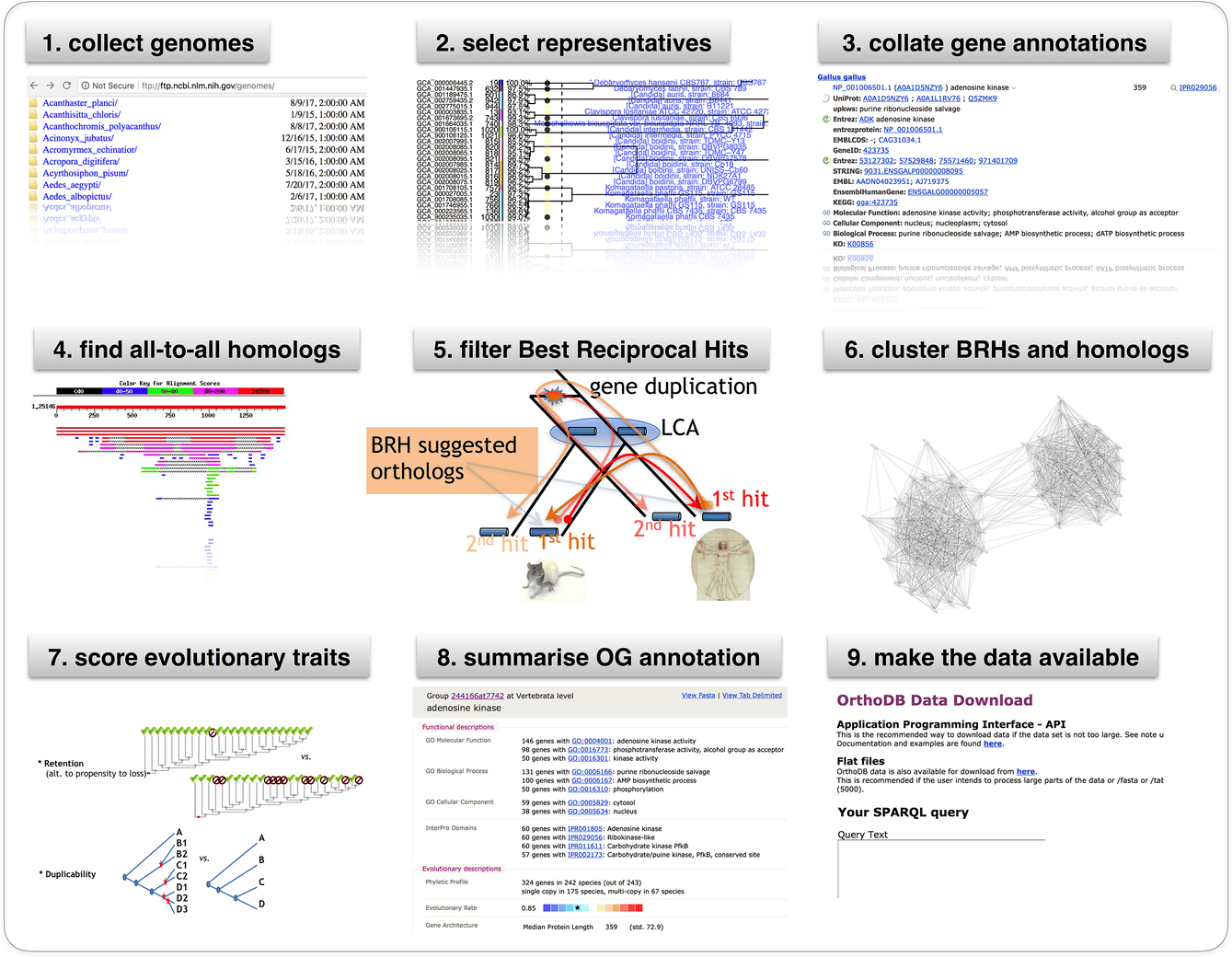
# Cite us
OrthoDB and BUSCO update: annotation of orthologs with wider sampling of genomes F Tegenfeldt, D Kuznetsov, M Manni, M Berkeley, EM Zdobnov, EV Kriventseva, NAR, Nov 2024, doi:10.1093/nar/gkae987 (opens new window). PMID:39535043 (opens new window)
..more & stats (opens new window)
# Documentation
# Contact
Email: support[at]orthodb.org Join the OrthoDB-News (opens new window) mailing list (low trafic). BUSCO issues board (opens new window) OrthoLoger issues board (opens new window)
# Scientific Advisory Board
- Stephen Richards from Baylor College of Medicine and UC Davis, USA.
- John H. (Jack) Werren from the University of Rochester, USA.
- John Kenneth Colbourne from the University of Birmingham, UK.
- Steven Marygold from the University of Cambridge, UK.
- Katharina Hoff from the University of Greifswald, Germany.


